History of India
- Introduction to Ancient India
- The Mauryan Empire
- Post-Mauryan India and the Golden Age
- Early Medieval India
- The Delhi Sultanate
- The Mughal Empire - Part I
- The Mughal Empire - Part II
- The Advent of European Powers
- The British Raj - Part I
- The British Raj - Part II
- Independence & Partition
The Mughal Empire - Part I
Jahangir and Shah Jahan: The Golden Age of Mughal Rule
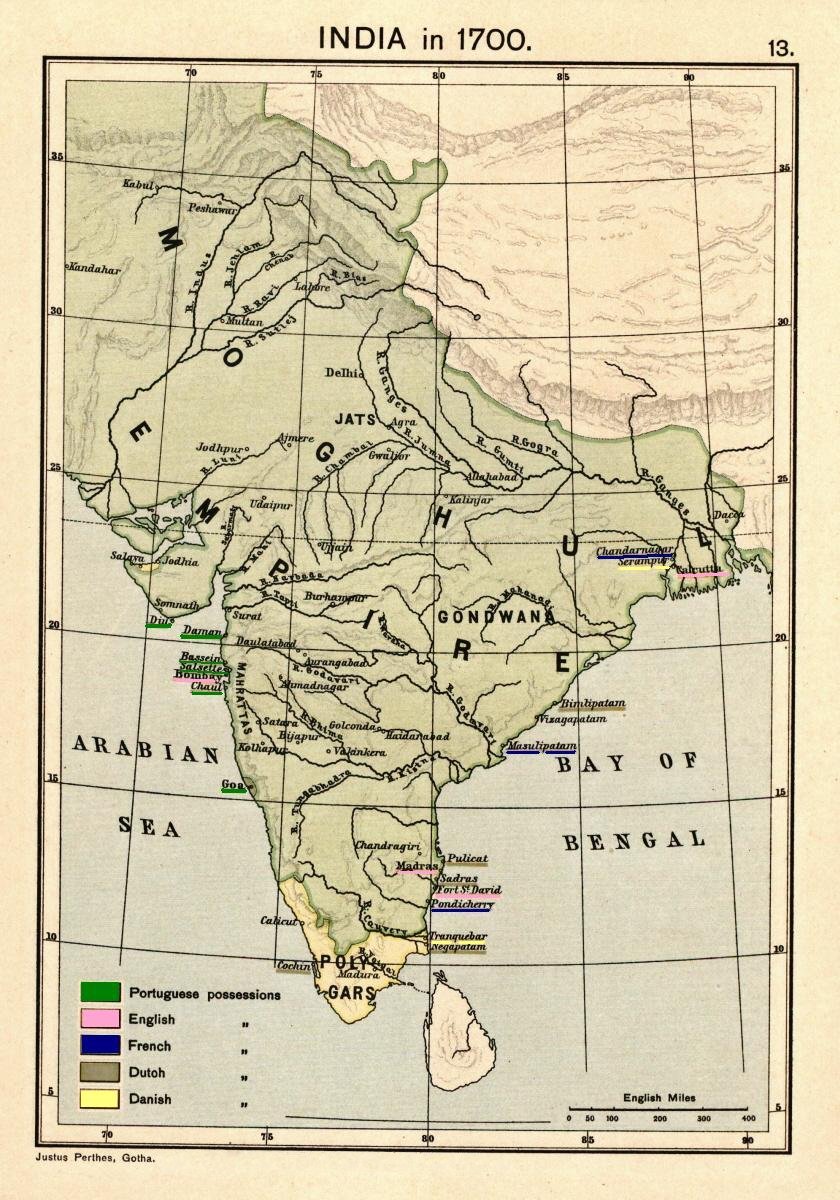
1526–1857 empire in South Asia.
The Mughal Empire, known for its grandeur and cultural richness, reached its zenith during the reigns of Jahangir and Shah Jahan. This period was marked by significant developments in administration, art, and architecture.
Jahangir's Rule
Jahangir, the fourth Mughal emperor, ruled from 1605 to 1627. His reign was marked by a keen interest in art, culture, and horticulture. Jahangir was known for his justice and was often referred to as the "World's Adjudicator." His memoir, Tuzuk-i-Jahangiri, provides a detailed account of his reign and is a significant historical document.
Jahangir's administration was marked by a fair and efficient system of justice. He introduced the "Chain of Justice," a bell outside his palace, which any citizen could ring to seek the emperor's attention to their grievances.
One of the most influential figures during Jahangir's reign was his wife, Nur Jahan. She was a powerful and astute woman who effectively ruled the empire during the later years of Jahangir's reign. Nur Jahan was instrumental in promoting art and culture in the Mughal court.
Shah Jahan's Rule
Shah Jahan, Jahangir's son, ascended the throne in 1628 and ruled until 1658. His reign is often referred to as the "Golden Age" of Mughal architecture. Shah Jahan commissioned several architectural marvels, including the Taj Mahal, the Red Fort, and the Jama Masjid.
The Taj Mahal, a mausoleum built in memory of his wife Mumtaz Mahal, is considered one of the Seven Wonders of the World. This magnificent structure, built with white marble and precious stones, is a testament to the architectural brilliance of the Mughal era.
Shah Jahan also commissioned the construction of the new capital city, Shahjahanabad (present-day Old Delhi). The city was designed with great attention to detail and was adorned with beautiful gardens, palaces, and mosques.
Shah Jahan's reign was also marked by a war of succession among his sons. His third son, Aurangzeb, emerged victorious, leading to Shah Jahan's imprisonment and the beginning of a new era in the Mughal Empire.
In conclusion, the reigns of Jahangir and Shah Jahan were significant periods in the history of the Mughal Empire. They were marked by advancements in administration, art, and architecture, contributing to the rich cultural heritage of India.