Nuclear Fusion
- Introduction to Nuclear Fusion
- Physics of Nuclear Fusion
- Energy from Nuclear Fusion
- Fusion Reactors
- Confinement and Heating
- Fusion Reactor Design
- Radiation and Safety
- Fusion Reactor Materials
- Fusion and the Environment
- Challenges in Nuclear Fusion
- The Future of Nuclear Fusion
The Future of Nuclear Fusion
Role of Fusion in the Future Energy Mix
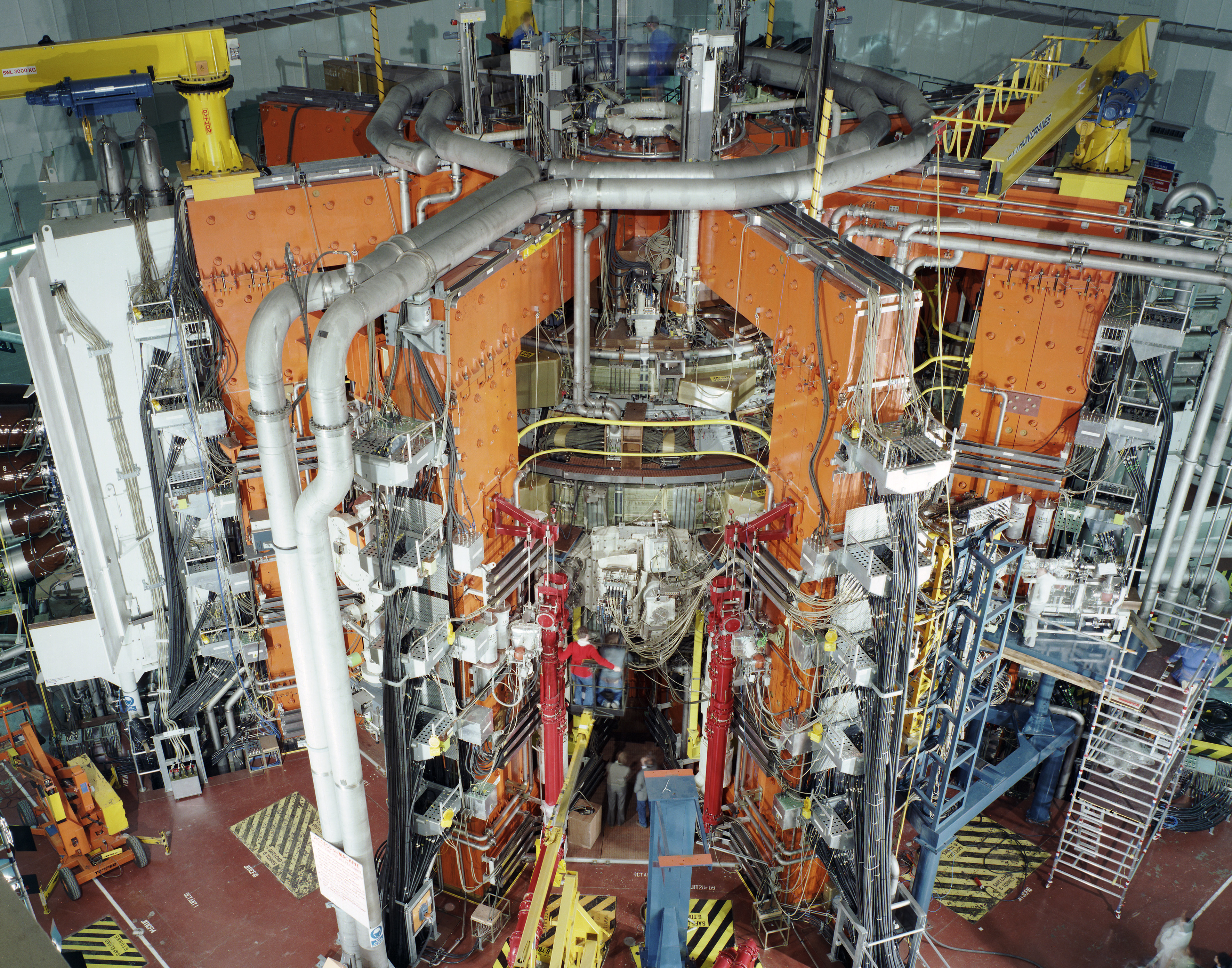
Experimental type of electricity generation using nuclear fusion.
As we look towards the future, the role of fusion in the global energy mix becomes an increasingly important topic of discussion. Fusion power, if harnessed successfully, could provide a nearly limitless and clean source of energy, fundamentally transforming our energy systems and helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Fusion Power vs. Other Renewable Energy Sources
When compared to other renewable energy sources, fusion power has several unique advantages. Unlike solar and wind power, fusion does not depend on weather conditions and can provide a constant, reliable source of energy. Furthermore, fusion power plants, once operational, could generate significantly more power than a similarly sized solar or wind farm.
However, it's important to note that fusion power is not intended to replace other renewable energy sources, but rather to complement them. The future energy mix will likely be a combination of various energy sources, each contributing to a stable, sustainable, and carbon-free energy system.
Environmental and Economic Benefits of Fusion Power
Fusion power has the potential to offer significant environmental benefits. Fusion reactions produce no greenhouse gas emissions, making fusion power a clean energy source. Additionally, fusion power produces no long-lived radioactive waste, addressing a key concern associated with current nuclear fission power plants.
From an economic perspective, fusion power could provide a cost-effective solution for meeting the world's growing energy demand. While the upfront costs of building fusion power plants are high, the virtually unlimited fuel supply (hydrogen isotopes deuterium and tritium can be extracted from seawater and lithium) could make fusion power economically competitive in the long run.
Policy Implications of a Shift Towards Fusion Power
The shift towards fusion power will have significant policy implications. Governments will need to invest in fusion research and development, and create regulatory frameworks for the construction and operation of fusion power plants. Policies will also need to address issues related to fusion fuel supply, waste management, and safety.
Moreover, international cooperation will be crucial for the success of fusion power. Given the high costs and technical challenges associated with fusion research, international collaborations like the ITER project are likely to play a key role in bringing fusion power to fruition.
In conclusion, while there are still many challenges to overcome, fusion power holds the promise of a sustainable, carbon-free energy future. As research progresses, the role of fusion in the future energy mix will become increasingly significant.