Adulting 101
- Introduction to the Course
- Learn to Cook
- Personal Finance and Budgeting
- Tax Management
- Emotional Health & Relationships
- Time Management
- Exercise
- Meditation
- Self-directed Learning
- Case Studies and Discussion
- Conclusion & Way Forward
Habit Forming
Ditching the Bad Habits
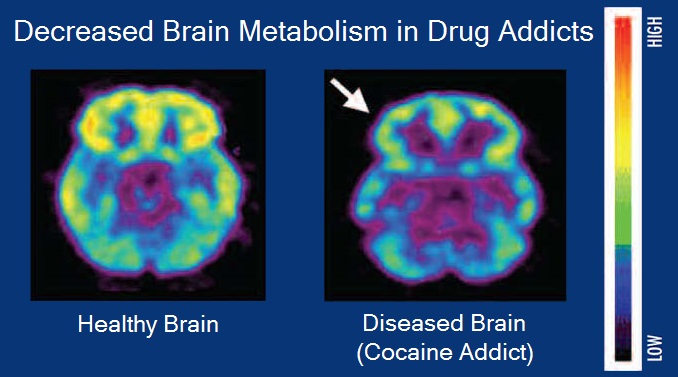
State characterized by compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli despite adverse consequences.
Bad habits can be a significant obstacle to achieving our goals and maintaining our well-being. They can range from minor annoyances to serious issues that impact our health and relationships. In this article, we will explore strategies for identifying and breaking bad habits, dealing with setbacks, and maintaining progress.
Identifying and Understanding Your Bad Habits
The first step in breaking a bad habit is to identify it. This may seem obvious, but many of our habits are so ingrained that we perform them unconsciously. Start by observing your behavior throughout the day and noting any actions that you think may be harmful or unproductive.
Once you've identified a bad habit, try to understand it. What triggers it? What reward do you get from it? Understanding the cue and reward in the habit loop can provide valuable insights into how to break it.
Strategies for Breaking Bad Habits
There are several strategies you can use to break bad habits:
-
Replacement: Find a healthier behavior to replace the bad habit. For example, if you have a habit of eating junk food when you're stressed, you could replace it with a healthier stress-relief habit like exercise or meditation.
-
Gradual Reduction: If the habit is too difficult to quit cold turkey, try gradually reducing the frequency or intensity of the habit. For example, if you're trying to quit smoking, you could start by reducing the number of cigarettes you smoke each day.
-
Negative Reinforcement: Associate the habit with a negative consequence. For example, you could make a pact with a friend to pay them a certain amount of money each time you perform the bad habit.
Dealing with Setbacks and Relapses
Breaking a bad habit is rarely a linear process. There will likely be setbacks and relapses along the way. It's important not to view these as failures, but as part of the process. When you have a setback, try to learn from it. What triggered the relapse? How can you avoid or handle that trigger in the future?
Maintaining Progress and Avoiding the Formation of New Bad Habits
Once you've broken a bad habit, the challenge is to maintain your progress and avoid falling back into old patterns. Regularly remind yourself of the reasons why you wanted to break the habit in the first place, and celebrate your progress to keep yourself motivated.
Also, be mindful of not replacing one bad habit with another. It's common for people to quit one addiction only to pick up another. Stay aware of your behavior and continue to cultivate healthy habits to support your well-being.
Breaking bad habits is a challenging but rewarding endeavor. With patience, persistence, and the right strategies, you can overcome your bad habits and create a healthier, more productive lifestyle.