Introduction to Dopamine
- Introduction to Neurotransmitters
- The Role of Dopamine
- The Role of Serotonin
- Interplay of Dopamine and Serotonin
- Competing Actions
- Collaborative Actions
- Conflicting Actions on Same Behaviors
- Complexity in Neuronal Combinations
- The Impacts of Therapeutic Drugs on Dopamine and Serotonin
- Dopamine, Serotonin and Mental Health
- Dopamine, Serotonin and Cognitive Functioning
- Settings, Synaptic Plasticity and Sensitization
- Prospects and Challenges in Dopamine & Serotonin Research
Introduction to Neurotransmitters
Introduction to Dopamine
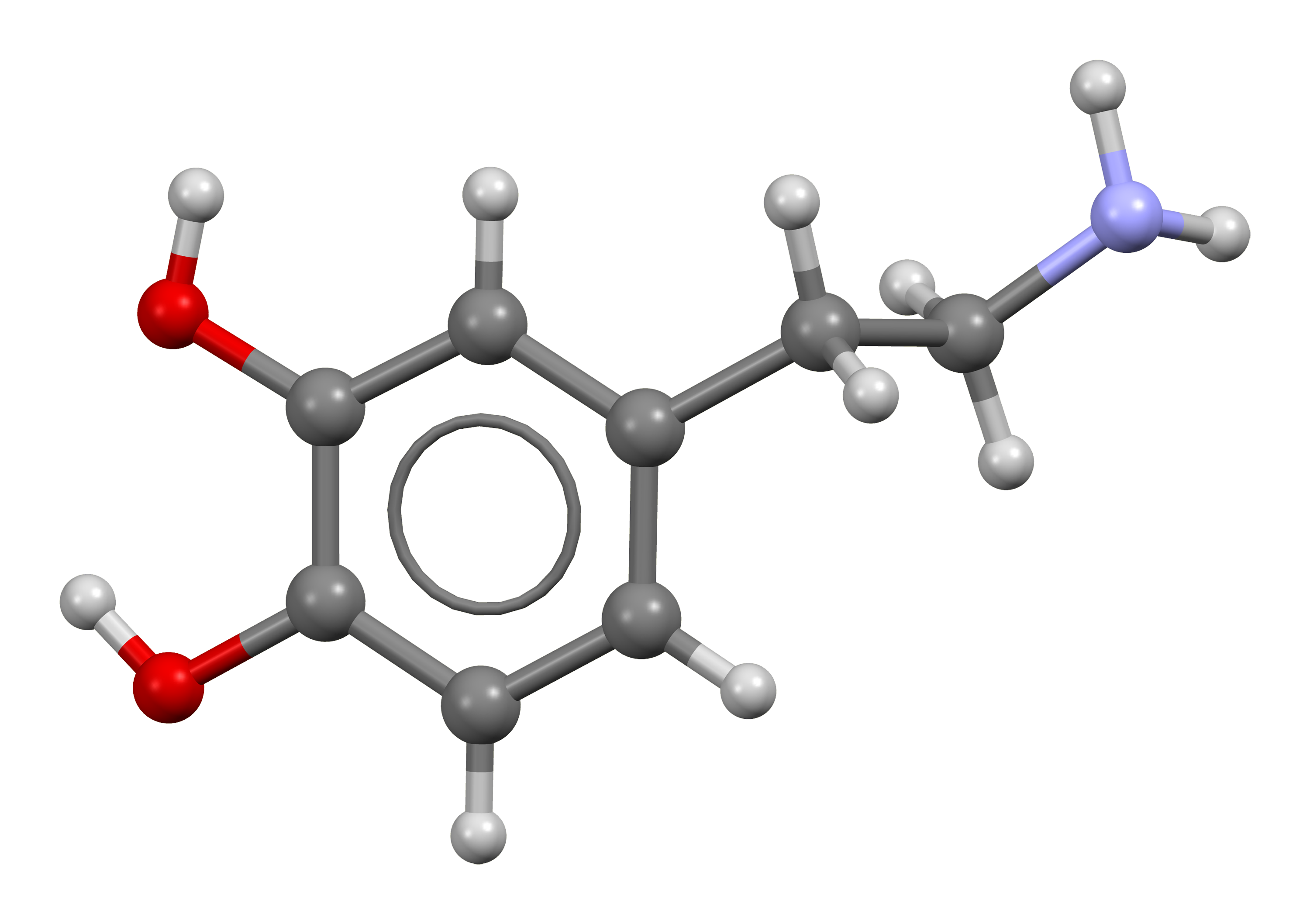
Organic chemical that functions both as a hormone and a neurotransmitter.
Dopamine is a type of neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger that transmits signals in the brain and other areas of the body. It plays several important roles in the body, and many significant functions in the brain are linked to dopamine.
Definition and Structure of Dopamine
Dopamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter, which means it contains one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain. It is derived from the amino acid tyrosine and is a precursor to other neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine and epinephrine. Structurally, dopamine is composed of a benzene ring with two hydroxyl side groups and an amine group.
Role of Dopamine in the Nervous System
Dopamine plays a crucial role in the nervous system, particularly in the brain where it affects a variety of functions including mood, sleep, attention, learning, and voluntary movement. It is also involved in the brain's reward system, which is why it is often associated with feelings of pleasure and reward.
Dopamine Pathways in the Brain
There are several major dopamine pathways in the brain. These include:
- The nigrostriatal pathway, which is involved in the control of movement. Dysfunction in this pathway is associated with movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease.
- The mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways, which are involved in reward, motivation, and emotion. These pathways are often implicated in psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and addiction.
- The tuberoinfundibular pathway, which is involved in the regulation of the hormone prolactin.
Effects of Dopamine on Behavior and Cognition
Dopamine has a significant impact on behavior and cognition. It is involved in the control of motor functions, the experience of pleasure, and the reinforcement of rewarding behaviors. It also plays a role in memory and learning, with higher levels of dopamine often linked to improved cognitive function and memory recall.
In summary, dopamine is a vital neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in our brain's function and our overall behavior. Understanding its function and pathways can provide valuable insights into human behavior and the development of various neurological and psychiatric disorders.