Nuclear Fusion Reactor Design
- Introduction to Fusion Energy
- The Tokamak Design
- The Stellarator Design
- The Inertial Confinement Fusion
- The Magnetic Confinement Fusion
- The Field-Reversed Configuration and Other Emerging Designs
- Safety, Waste and Environmental Impact
- Future of Fusion & Course Review
Safety, Waste and Environmental Impact
Safety Procedures in Fusion Reactors
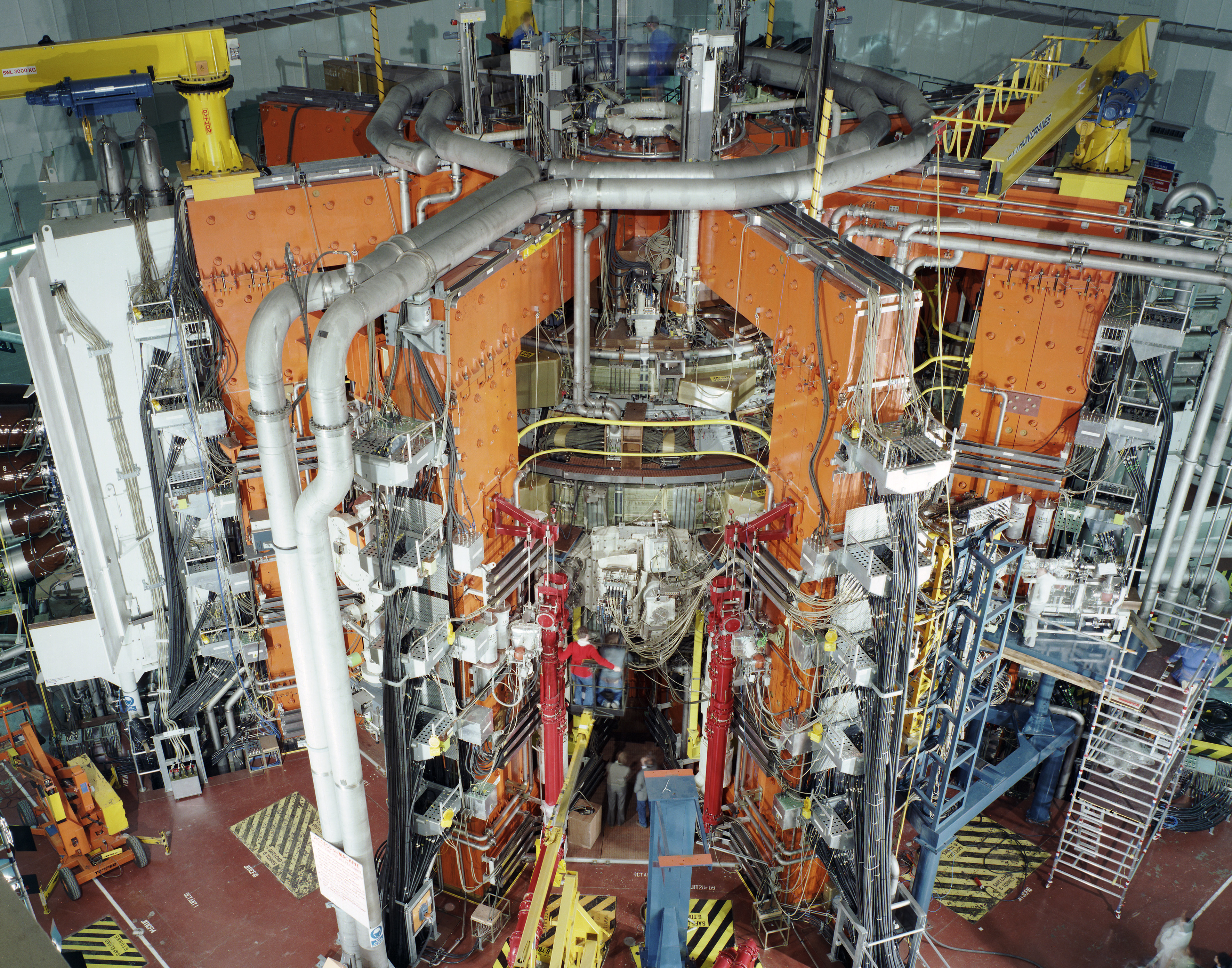
Experimental type of electricity generation using nuclear fusion.
Safety is a paramount concern in any energy production facility, and fusion reactors are no exception. This article will provide an overview of the safety procedures and protocols in fusion reactors, discuss the safety measures in different fusion reactor designs, and present case studies of safety incidents and how they were managed.
Importance of Safety in Fusion Reactor Operations
Fusion reactors, like any large-scale industrial operation, have inherent risks. These risks can be mitigated through careful design, rigorous safety protocols, and ongoing staff training. The goal is to prevent accidents that could harm personnel, damage the reactor, or release radioactive materials.
Safety Procedures and Protocols in Fusion Reactors
Safety procedures in fusion reactors are designed to prevent accidents and to respond effectively if an accident does occur. These procedures include:
-
Routine Maintenance and Inspection: Regular checks are performed to ensure that all components of the reactor are functioning correctly. This includes inspecting the reactor's containment structure, cooling systems, and magnetic field generators.
-
Emergency Response Plans: Every fusion reactor has a detailed plan for responding to emergencies. This includes procedures for evacuating personnel, shutting down the reactor, and containing any potential release of radioactive materials.
-
Staff Training: All staff working at a fusion reactor undergo rigorous training. They are taught how to operate the reactor safely, how to respond in an emergency, and how to use protective equipment.
Safety Measures in Different Fusion Reactor Designs
Different fusion reactor designs have different safety considerations. For example, tokamak reactors, which use magnetic fields to contain the plasma, must be carefully monitored to prevent disruptions that could damage the reactor's walls. Stellarator reactors, on the other hand, have a more stable plasma but are more complex and require more extensive safety checks.
Case Studies of Safety Incidents
While fusion reactors are designed with safety in mind, incidents can still occur. One notable example is the 2013 incident at the National Ignition Facility in the United States, where a small amount of radioactive tritium was released during a routine maintenance operation. The incident was quickly contained, and no staff were exposed to harmful levels of radiation. This incident highlighted the importance of rigorous safety procedures and effective emergency response plans.
In conclusion, safety is a critical aspect of fusion reactor operations. Through careful design, rigorous safety protocols, and ongoing staff training, the risks associated with fusion reactors can be effectively managed.