Nuclear Fusion Reactor Design
- Introduction to Fusion Energy
- The Tokamak Design
- The Stellarator Design
- The Inertial Confinement Fusion
- The Magnetic Confinement Fusion
- The Field-Reversed Configuration and Other Emerging Designs
- Safety, Waste and Environmental Impact
- Future of Fusion & Course Review
Safety, Waste and Environmental Impact
Environmental Impact of Fusion Reactors
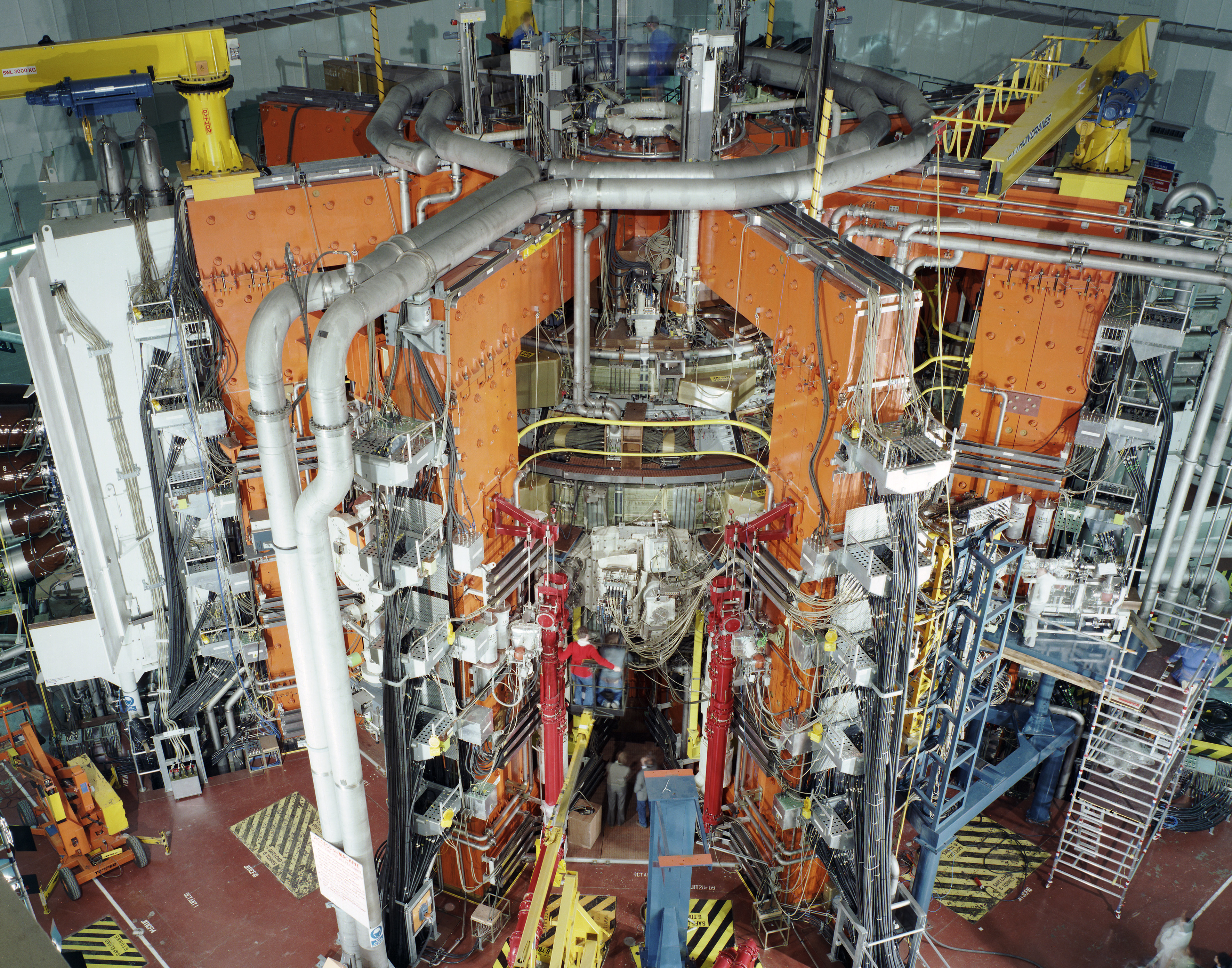
Experimental type of electricity generation using nuclear fusion.
Fusion energy, often hailed as the 'holy grail' of sustainable energy, promises to provide a nearly limitless and clean source of power. However, like all energy sources, it's essential to understand its potential environmental impact. This article will delve into the environmental implications of fusion energy, comparing it with other energy sources, and examining the lifecycle environmental impact of fusion reactors.
Fusion Energy and the Environment
Fusion energy is often touted as a clean energy source because it produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation. The primary byproduct of fusion is helium, an inert and non-toxic gas. This is a stark contrast to fossil fuels, which release large amounts of carbon dioxide and other pollutants when burned.
However, it's important to note that while fusion reactors themselves do not emit greenhouse gases, the processes involved in building and maintaining these reactors do. This includes the extraction and processing of raw materials, construction of the reactor, and eventual decommissioning and waste management.
Comparison with Other Energy Sources
When compared to other energy sources, fusion energy has several advantages. Unlike fossil fuels, fusion does not contribute to climate change or air pollution. Compared to nuclear fission, fusion does not produce long-lived radioactive waste and there is no risk of a meltdown.
Renewable energy sources such as wind and solar are also clean and sustainable, but they are intermittent, meaning they can't produce power all the time. Fusion energy, on the other hand, has the potential to provide a constant and reliable source of power.
Lifecycle Environmental Impact of Fusion Reactors
The lifecycle environmental impact of a fusion reactor includes all stages from construction to decommissioning. The construction phase involves the extraction and processing of raw materials, which can have environmental impacts. However, these are likely to be similar or less than those associated with the construction of other types of power plants.
During operation, fusion reactors do not produce greenhouse gases or air pollutants. However, they do produce a small amount of radioactive waste. This waste is short-lived, decaying to safe levels within a few hundred years, unlike the long-lived waste produced by fission reactors.
The decommissioning phase involves dismantling the reactor and managing the waste. The environmental impact of this phase is largely dependent on the waste management practices in place.
In conclusion, while fusion energy does have some environmental impacts, they are significantly less than those associated with fossil fuels and nuclear fission. With further research and development, fusion energy has the potential to provide a sustainable and environmentally friendly source of power.