Parenting a toddler 101
- Introduction to Modern Parenting
- Understanding Toddlers
- Healthy Sleep Habits
- Nutritional Needs for Toddlers
- Managing Food Picky Eaters
- Active Play and Exercise
- Positive Discipline Techniques
- Emotional Well-being and Resilience
- Fostering Social Skills
- Preparing for Preschool
- Child Safety Basics
- Basic Emergency Protocols
- Conclusion and Taking the Next Steps
Nutritional Needs for Toddlers
Managing Food Allergies in Toddlers
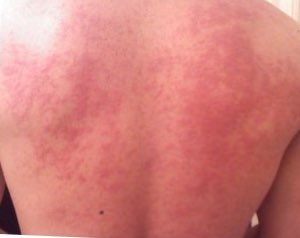
Hypersensitivity reaction type I disease that is an abnormal response to a food, triggered by the body's immune system.
Food allergies in toddlers can be a source of worry for parents. Understanding the common food allergies, recognizing their symptoms, and knowing how to manage them can help alleviate these concerns. This article provides a comprehensive guide to managing food allergies in toddlers.
Common Food Allergies in Toddlers
The most common food allergies in toddlers include milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, soy, wheat, fish, and shellfish. These eight foods account for about 90% of all food allergies in children. It's important to note that a child can be allergic to any food, but these are the most common.
Recognizing Symptoms of Food Allergies
Symptoms of food allergies can appear within a few minutes to a few hours after eating the food. Common symptoms include:
- Hives (red spots that look like mosquito bites)
- Itchy skin rashes (eczema, also called atopic dermatitis)
- Swelling
- Breathing problems
- Sneezing
- Watery eyes
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
In severe cases, a child might experience anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening reaction that can cause difficulty in breathing and swallowing, and loss of consciousness. If you suspect your child is experiencing anaphylaxis, seek immediate medical attention.
How to Manage and Prevent Food Allergies
If you suspect your child has a food allergy, consult a healthcare provider. They can perform tests to confirm the allergy and provide guidance on managing it. Here are some general strategies:
-
Avoid the allergen: Once a food allergy is confirmed, the most effective management strategy is to avoid the allergen. Read food labels carefully to ensure the allergen is not present.
-
Educate your child: As your child grows older, teach them about their allergy and the importance of avoiding the allergen. They should also know to ask adults if a food contains the allergen.
-
Create an action plan: Work with your healthcare provider to create an action plan in case of accidental exposure. This might include administering medication like an antihistamine or, in severe cases, an epinephrine auto-injector.
When and How to Introduce Potential Allergenic Foods
Recent research suggests that introducing potential allergenic foods early (around 6 months of age) might help prevent food allergies. However, this should be done carefully and under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Start with small amounts and watch for any reaction.
Remember, every child is unique, and what works for one might not work for another. Always consult with a healthcare provider when dealing with food allergies.
By understanding and managing food allergies, you can help ensure your toddler enjoys a variety of foods while staying safe.