Blood Chemistry 101 from a Functional Medicine Perspective
- Introduction to Blood Test Analysis
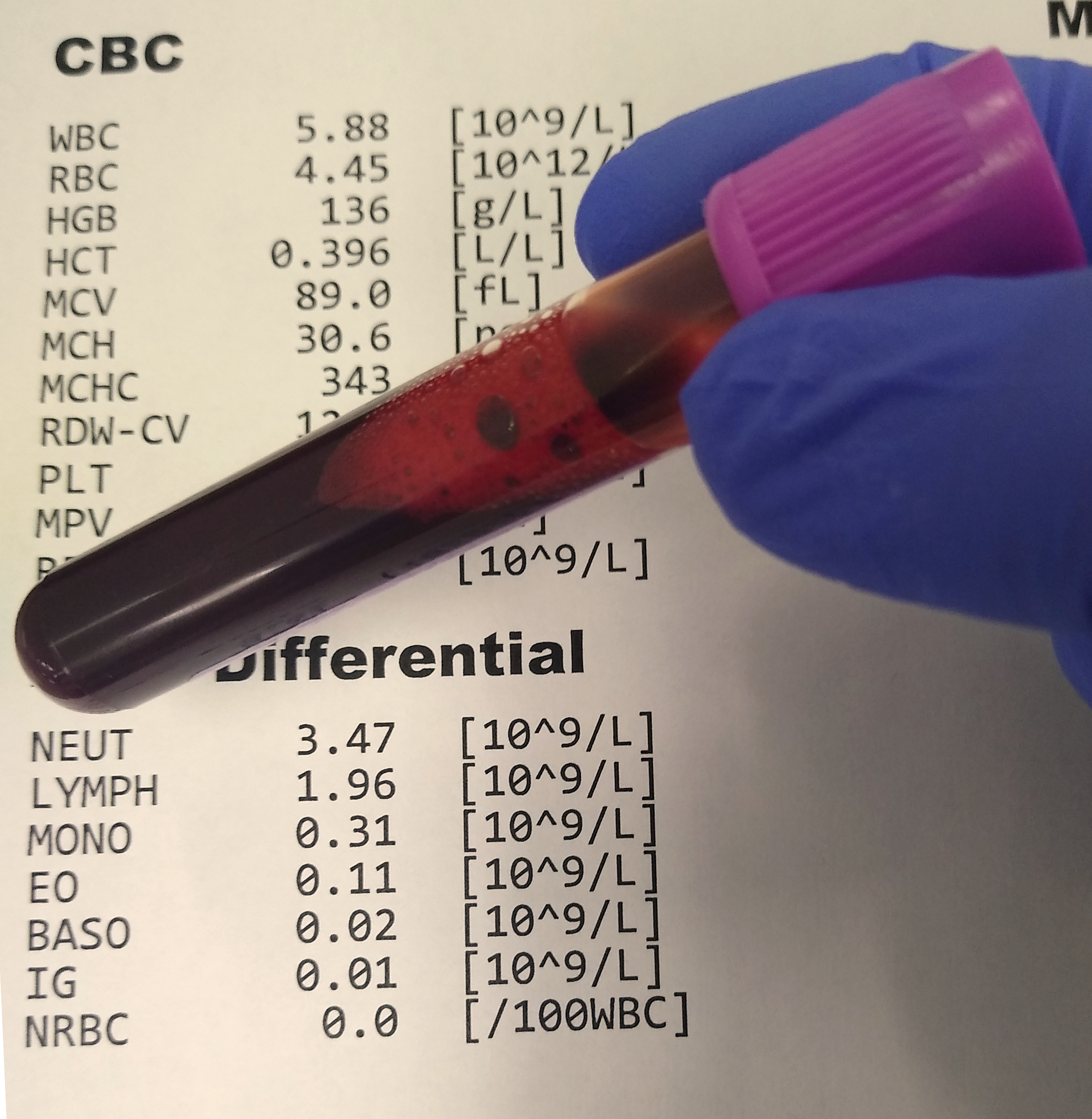
- Understanding Complete Blood Count (CBC)
- Insight into Complete Metabolic Panel (CMP)
- Studying Vitamin D
- Inflammation Markers - CRP
- Decoding Thyroid Markers
- Iron Markers
- Lipid Panel Assessment
- Micronutrient Markers: Folate, Vitamin B12
- Micronutrient Markers: Zinc, Copper, Magnesium
- Other Key Blood Chemistry Markers
- Implementing Lifestyle Recommendations for Improved Markers
- Pulling It All Together – Your Personal Health Assessment
Pulling It All Together – Your Personal Health Assessment
Comprehensive Review of Blood Markers and Their Significance
Medical laboratory test.
As we reach the end of our journey to understand blood markers and their implications on our health, it's time to revisit the key concepts we've learned throughout the course. This comprehensive review will serve as a refresher, helping you consolidate your understanding of each blood marker, their normal and abnormal ranges, and their implications from a functional medicine perspective.
Recap of Each Blood Marker and Its Significance
We started our journey with the Complete Blood Count (CBC), a common blood test that provides information about different types of cells in the blood. It includes measurements of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Each of these components plays a crucial role in our health, from carrying oxygen to fighting infections and aiding in clotting.
Next, we delved into the Complete Metabolic Panel (CMP), which gives us insight into the body's metabolism and chemical balance. It includes tests for liver function, kidney function, blood sugar levels, and electrolyte balance.
We also explored various specific markers, such as Vitamin D, inflammation markers like CRP, Thyroid markers, Iron Markers, and Lipid panel. Each of these markers provides unique insights into our health, from bone health and immune function to thyroid health, iron levels, and cardiovascular health.
Lastly, we looked at micronutrient markers such as folate, vitamin B12, zinc, copper, and magnesium. These markers are essential for various bodily functions, including DNA synthesis, immune function, wound healing, and nerve function.
Review of Normal and Abnormal Ranges for Each Marker
Understanding the normal and abnormal ranges for each marker is crucial for interpreting blood test results. Throughout the course, we've discussed the typical laboratory ranges for each marker and what it might mean if these ranges are high or low.
For instance, a high count of white blood cells in a CBC test might indicate an infection, while low levels could suggest a weakened immune system. Similarly, high levels of CRP, an inflammation marker, could indicate inflammation in the body, while low levels are generally considered healthy.
Implications from a Functional Medicine Perspective
From a functional medicine perspective, blood markers are more than just numbers on a lab report. They provide valuable insights into our overall health and can guide us in making lifestyle changes to improve our wellbeing.
For example, if your Vitamin D levels are low, you might need to spend more time in the sun or consider a Vitamin D supplement. If your lipid panel shows high levels of LDL cholesterol, you might need to make dietary changes or increase your physical activity.
In conclusion, understanding your blood markers and their significance is a powerful tool for taking control of your health. By knowing what each marker means and how to interpret it, you can make informed decisions about your lifestyle and healthcare.