English 101
- Introduction to Intermediate English
- Intermediate English Writing
- Intermediate English Speaking
- Intermediate English Reading
- Practical Intermediate English
- Introduction to Advanced English
- Advanced English Writing
- Advanced English Speaking
- Advanced English Reading
- Practical Advanced English
- Proficient Use of English
- English in Practice
Proficient Use of English
Understanding Native English Speakers
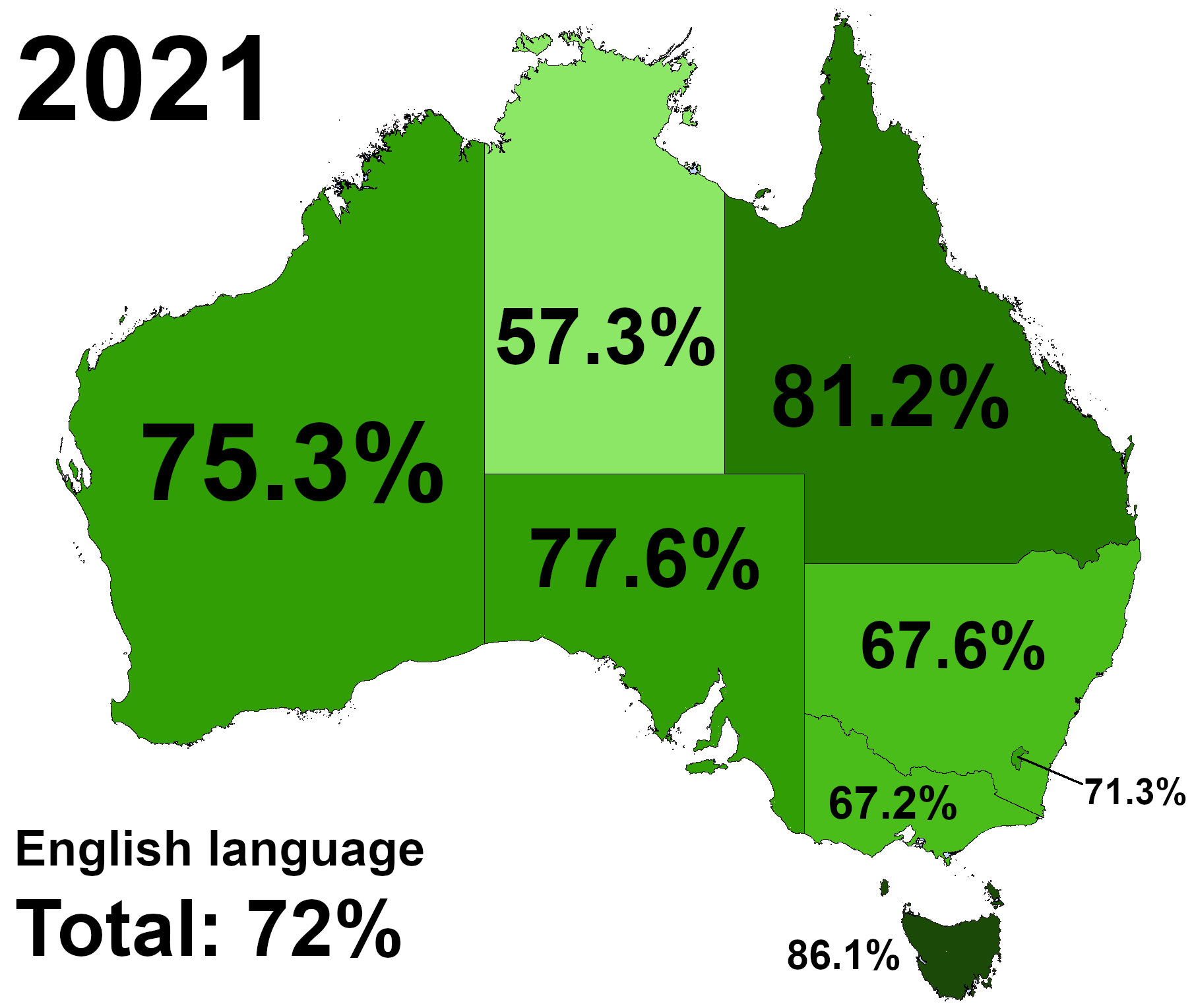
Dialect of English language spoken in Australia.
Understanding native English speakers can be a challenging task due to the variety of accents, slang, and colloquialisms used. This unit aims to equip you with the necessary skills to comprehend and interact with native English speakers effectively.
Comprehending Accents
English is spoken in many parts of the world, and each region has its unique accent. The most commonly recognized accents are American, British, and Australian.
- American English: Characterized by rhotic pronunciation (pronouncing the 'r' at the end of words), and certain vowel shifts.
- British English: Known for its non-rhotic pronunciation (not pronouncing the 'r' at the end of words), and unique vowel and consonant sounds.
- Australian English: Shares features with both British and American English but also has distinctive vowel sounds and intonation.
Understanding these accents requires exposure and practice. Listening to podcasts, watching movies, or engaging in conversations with native speakers can help you familiarize yourself with these accents.
Understanding Slang and Colloquialisms
Slang and colloquialisms are informal words or phrases used in everyday conversation. They can vary greatly from region to region, even within the same country. Here are a few examples:
- American Slang: "What's up?" (How are you?), "Hang out" (spend time), "Bail" (leave abruptly)
- British Slang: "Bloke" (man), "Cheerio" (goodbye), "Chuffed" (pleased)
- Australian Slang: "G'day" (hello), "Arvo" (afternoon), "Barbie" (barbecue)
Understanding slang and colloquialisms can be challenging, but it's essential for comprehending native speakers. Reading books, watching TV shows, and using language learning apps can help you learn and understand these expressions.
Practice
To improve your comprehension skills, engage in active listening. This involves paying full attention to the speaker, understanding the context, and asking clarifying questions if necessary.
- Listen to Conversations: Listen to conversations between native English speakers. This could be through movies, TV shows, podcasts, or in-person interactions.
- Analyze the Conversation: Try to understand the context, identify the slang or colloquial expressions used, and note the accent.
- Practice Speaking: Try to mimic the accents and use the slang or colloquial expressions in your conversations.
Remember, understanding native English speakers is a skill that develops over time. Be patient with yourself, practice regularly, and don't be afraid to ask questions.