Chemistry 101 for Teens
- Introduction to Chemistry
- The Periodic Table
- Atomic Structure
- Chemical Bonding
- Chemical Reactions
- Solutions and Solubility
- Acids, Bases, and pH
- Energy in Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry Basics
- Biochemistry Basics
- Chemistry in Our Daily Life
The Periodic Table
History of the Periodic Table
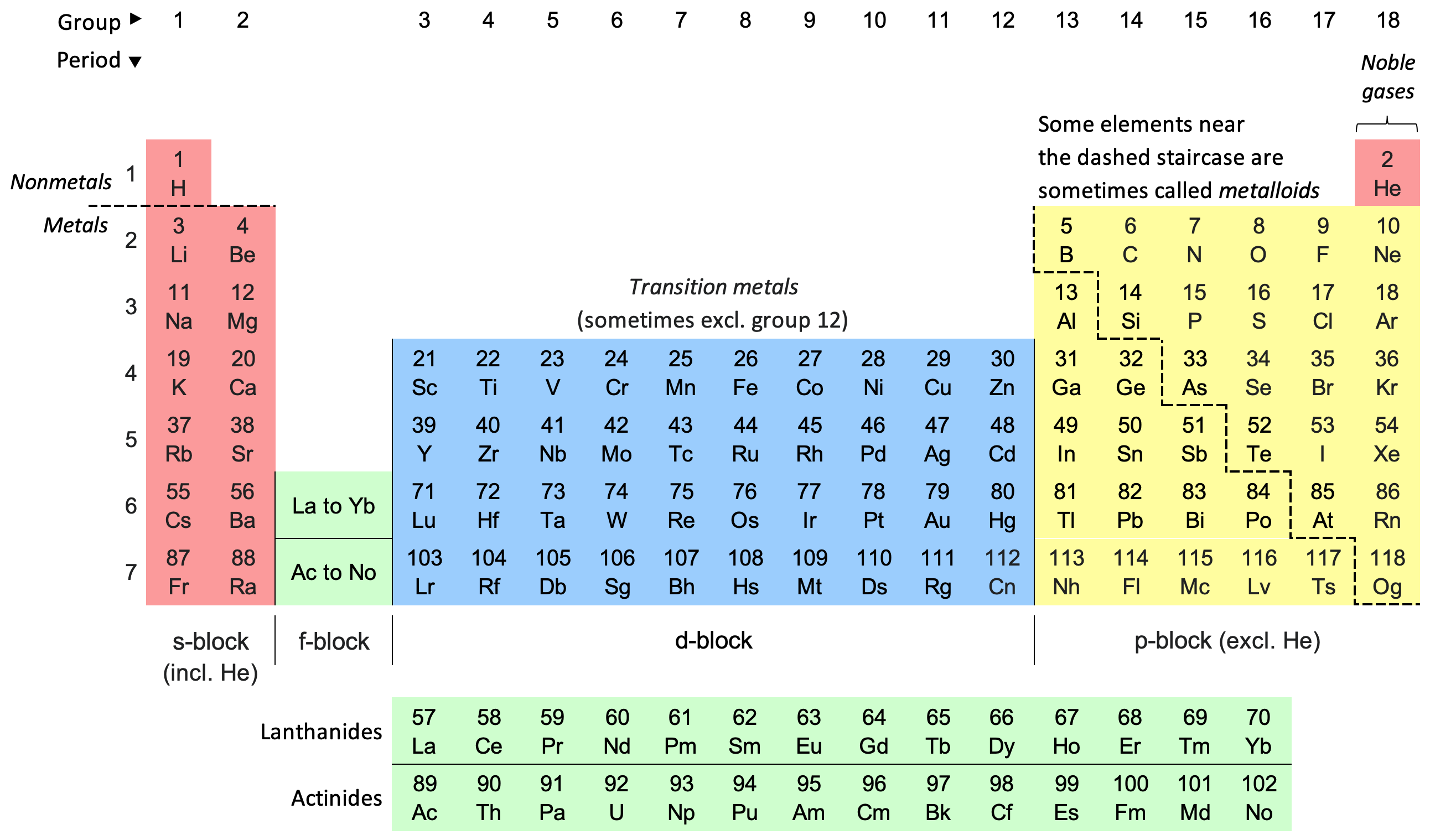
Table systematically placing elements based on atomic number and recurrent properties.
The Periodic Table of Elements, a cornerstone of chemistry, is a systematic way to organize and understand the behavior of different elements. Its development is a fascinating story that spans centuries and involves several notable scientists.
Early Attempts at Organizing Elements
The first attempts to classify elements date back to ancient times when philosophers like Aristotle classified matter into four elements: earth, air, fire, and water. However, the first scientific approach to classify elements was made by Antoine Lavoisier in the late 18th century. He grouped elements into metals, non-metals, and gases.
Mendeleev's Periodic Table
The most significant advancement in the classification of elements came from Dmitri Mendeleev in the mid-19th century. Mendeleev arranged elements in order of increasing atomic weight and noticed that certain properties repeated periodically. He left gaps in his table for elements that had not yet been discovered, accurately predicting their properties. This was a revolutionary concept and marked the birth of the Periodic Table as we know it.
The Modern Periodic Table: Moseley's Contribution
The modern Periodic Table, however, is not organized by atomic weight, but by atomic number. This change was due to the work of Henry Moseley in the early 20th century. Moseley discovered that each element has a unique atomic number, which is equal to the number of protons in an atom's nucleus. This led to the reorganization of the Periodic Table based on atomic number, resolving inconsistencies in Mendeleev's table.
The Periodic Table has evolved over time, with new elements being added as they are discovered. Today, it organizes 118 confirmed elements, from Hydrogen with an atomic number of 1, to Oganesson with an atomic number of 118.
In conclusion, the history of the Periodic Table is a testament to the progress of scientific understanding. From early attempts to classify elements to the modern Periodic Table, this tool continues to be a fundamental part of chemistry, helping scientists predict the properties of elements and their compounds.