Chemistry 101 for Teens
- Introduction to Chemistry
- The Periodic Table
- Atomic Structure
- Chemical Bonding
- Chemical Reactions
- Solutions and Solubility
- Acids, Bases, and pH
- Energy in Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry Basics
- Biochemistry Basics
- Chemistry in Our Daily Life
The Periodic Table
Major Groups of the Periodic Table
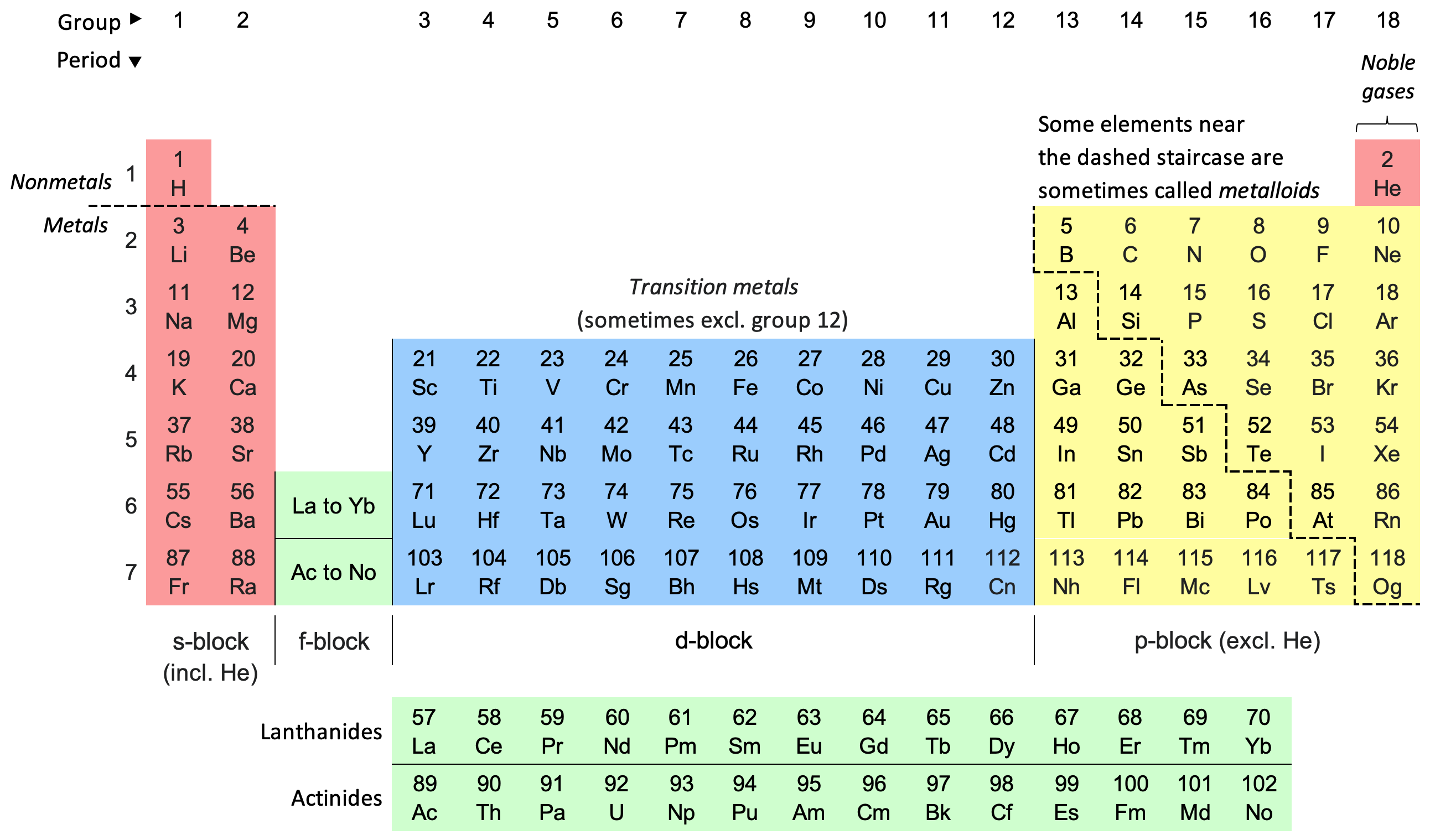
Table systematically placing elements based on atomic number and recurrent properties.
The Periodic Table of Elements is a systematic way of organizing chemical elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The table is divided into several groups that contain elements with similar properties. Here, we will explore the major groups of the Periodic Table.
Alkali Metals (Group 1)
Alkali metals are located in the first group of the Periodic Table. They include lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). These metals are highly reactive due to their single electron in their outermost shell. They are soft, have low melting points, and are good conductors of heat and electricity.
Alkaline Earth Metals (Group 2)
The alkaline earth metals are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). They are located in the second group of the Periodic Table. These metals have two electrons in their outer shell, making them less reactive than alkali metals. They are harder than alkali metals and have higher melting points.
Transition Metals (Groups 3-12)
Transition metals are located in groups 3-12 of the Periodic Table. They include elements like iron (Fe), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), and gold (Au). These metals are characterized by their ability to form stable, colored compounds, and they often have multiple oxidation states.
Halogens (Group 17)
Halogens are located in the 17th group of the Periodic Table. They include fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). Halogens are highly reactive nonmetals with seven electrons in their outermost shell. They readily gain an electron to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Noble Gases (Group 18)
Noble gases are located in the 18th group of the Periodic Table. They include helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn). Noble gases are characterized by their full electron shells, making them very stable and unreactive.
Lanthanides and Actinides (Periods 6 and 7)
The lanthanides and actinides are two series of elements located at the bottom of the Periodic Table. The lanthanides, also known as rare earth metals, include elements 57-71. The actinides include elements 89-103. Many of these elements are synthetic and highly radioactive.
Understanding the major groups of the Periodic Table is crucial for understanding the properties of elements and how they interact with each other. Each group has unique characteristics that define the behavior of the elements within it.